8 major Google algorithm updates, explained
Of countless Google algorithm updates introduced over the last decade, here are the ones that changed SEO forever.
Google claims to update its search algorithm several thousand times per year. In the absolute majority of cases, Google algorithm updates are too small to notice. But, every once in a while, Google introduces a change so fundamental, that it disrupts the way we do SEO forever.
In this post, we will be counting down eight of the most critical search algorithm changes. We will look into why these updates were introduced, how they work and what adjustments we had to make to our SEO strategies in response.
But before we start, let’s see if you’ve ever been impacted by an algorithm update. All you need to do is launch Rank Tracker, sync it with your Google Analytics account and switch to Organic Traffic.
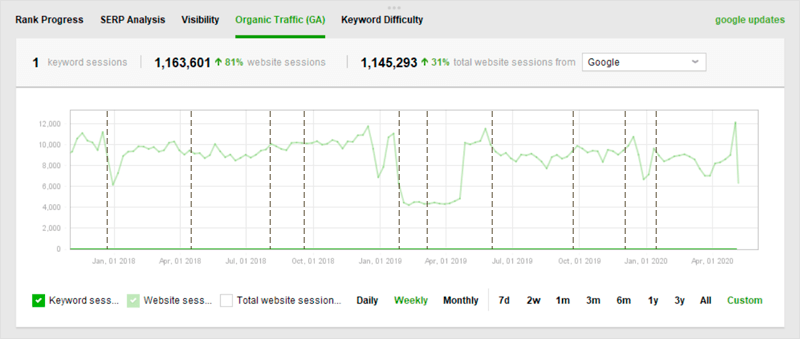
Just hover your mouse over the dash lines on the graph to see if certain algo updates correspond with your site’s traffic changes.
1. Panda
Date: February 24, 2011
Hazards: Duplicate, plagiarized or thin content; user-generated spam; keyword stuffing.
How it works: The Panda algorithm update assigns a so-called “quality score” to web pages. This score is then used as a ranking factor. Initially, the effects of Panda were mild, but in January 2016 it was permanently incorporated into Google’s core algorithm. Since then, update rollouts have become more frequent, so both Panda penalties and recoveries now happen faster.
How to adjust: Run regular site checks for content duplication, thin content, and keyword stuffing. To do that, you’ll need a site crawler, like SEO PowerSuite’s Website Auditor.

With the WebSite Auditor’s new Content Editor module, you can also avoid a potential penalty and create pages without the risk of accidental keyword stuffing. Content Editor analyzes the pages of your top competitors and provides SEO recommendations based on the content that’s already successful in Google search.

And if you want to check whether your content is duplicated elsewhere on the web, use a plagiarism checker like Copyscape.
2. Penguin
Date: April 24, 2012
Hazards: Spammy or irrelevant links; links with over-optimized anchor text.
How it works: Google Penguin’s objective is to down-rank sites whose backlinks look unnatural. This update put an end to low-effort link building, like buying links from link farms and PBNs.
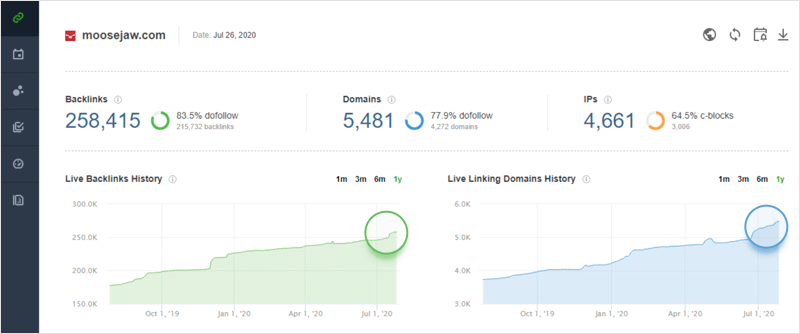
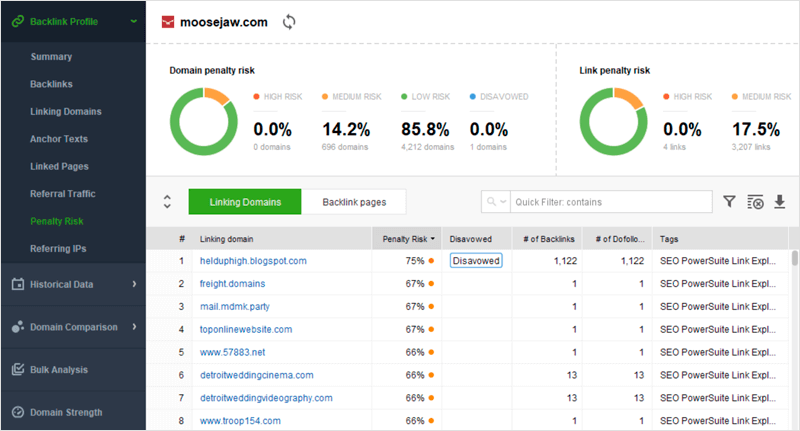
How to adjust: To stay safe from the effects of the Google Penguin update, monitor your link profile’s growth and run regular audits with a backlink checker like SEO SpyGlass. In the tool’s Summary dashboard, you’ll find a progress graph for your link profile’s growth. Look out for any unusual spikes: those might be the result of a negative SEO attack by your competitors.
The stats that we know Penguin takes into account are incorporated into SEO SpyGlass’s Penalty Risk formula. Navigate to the Penalty Risk tab and sort your backlink list from highest risk to lowest. Links with a risk above 50% should be investigated. If they turn out to be malicious, add them to the disavow file, download it, and submit it to Google’s Disavow Links Tool.
3. Hummingbird
Date: August 22, 2013
Hazards: Keyword stuffing; low-quality content.
How it works: The Hummingbird algorithm helps Google better interpret search queries and provide results that match searcher intent (as opposed to the individual terms within the query). While keywords continue to be important, the Hummingbird algorithm makes it possible for a page to rank for a query even if it doesn’t contain the exact words the searcher entered. This is achieved with the help of natural language processing that relies on latent semantic indexing, co-occurring terms and synonyms.
How to adjust: Expand your keyword research and focus on concepts behind the keywords. Carefully analyze related searches, synonyms and co-occurring terms. Great sources of such ideas are Google Related Searches and Google Related Questions, as well as Google Autocomplete suggestions. You’ll find all of them incorporated into Rank Tracker’s Keyword Research module.

Use these insights to better understand your audience’s language and diversify your content. By creating comprehensive content that satisfies searcher intent, you’ll win both in terms of engagement and SEO.
4. Mobile
Date: April 21, 2015
Hazards: Lack of a mobile version of the page; poor mobile usability.
How it works: This, and subsequent mobile search updates (2018, 2020) have shifted the focus from a desktop to a mobile version of your website. Today, Google ranks all websites based on how fast and user-friendly their mobile versions are.
How to adjust: Optimize your pages for mobile search and focus on speed and usability. Google’s mobile-friendly and page speed tests will help you see which aspects of your page need to be improved. The tests are integrated into WebSite Auditor so you can check your pages’ mobile optimization as a part of your overall website audit. You’ll find it in Content Analysis > Page Audit:
 100vw, 800px” data-lazy-src=”https://searchengineland.com/wp-content/seloads/2020/10/mobile-website-auditor-image7.png” /></figure>
</div>
<h2 id=) 5. RankBrain
5. RankBrain
Date: October 26, 2015
Hazards: Lack of query-specific relevance; shallow content; poor UX.
How it works: RankBrain is a part of Google’s Hummingbird algorithm. It is a machine learning system that helps Google understand the meaning behind queries and serve best-matching search results in response to those queries. Google calls RankBrain the third most important ranking factor.
While we don’t know the exact formula behind this major update, the consensus is that RankBrain is responsible for customizing a user’s Google search results. Basically, Google goes beyond a person’s search query and takes into account the larger context, like synonyms, implied words, and personal search history.
How to adjust: Optimize your pages for relevance and comprehensiveness with the help of competitive analysis. With the WebSite Auditor‘s TF-IDF tool, you can discover entire lists of relevant terms and concepts used by a large number of your top-ranking competitors. Find a way to add these terms to your content and you will see your search relevance increase dramatically.
 100vw, 800px” data-lazy-src=”https://searchengineland.com/wp-content/seloads/2020/10/rank-brain-website-auditor-image8.png” /></figure>
</div>
<h2 id=) 6. Medic
6. Medic
Date: May 4, 2018
Hazards: Lack of authority on YMYL websites; weak E-A-T signals.
How it works: The Google Medic update seemed to disproportionately affect medical websites as well as other websites that have to do with potentially life-altering decisions (finance, law, education). Although not explicitly confirmed, Google representatives have hinted that the update implemented some of the E-A-T (expertise, authority, trust) signals from the Quality Rater Guidelines document.
How to adjust: To date, there is no proven recovery strategy for the Medic update. Some SEOs suggest hiring expert writers to lend credibility to your website, others claim the solution is in building entities for your brand. But, if we were to stick to the facts, the only reliable way to increase the authority of your website is by growing your backlink profile. An efficient approach would be to use a backlink research tool, like SEO SpyGlass, and borrow backlink ideas from your competitors.
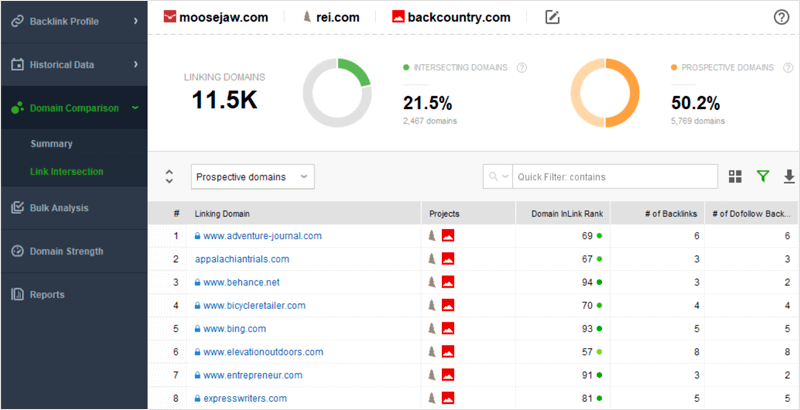
SEO SpyGlass allows you to find the backlink gap between your website and your competitors’ websites. The best prospects are the high-authority websites that link to two or more of your competitors. This indicates that the websites are interested in your niche, but do not have an exclusive relationship with any one company.
For more tips, explore this SEO guide based on the Quality Rater Guidelines.
7. Bert
Date: October 22, 2019
Hazards: Poorly written content; lack of focus; lack of context.
How it works: This Google algorithm update uses natural language processing technology to better understand search queries, interpret text, identify entities and relationships between entities. We’ve seen Panda, Hummingbird and RankBrain updates move away from keywords, and the BERT update is the culmination of this effort — it allows Google to understand much more nuance in both queries and search results.
How to adjust: We’ve finally lived to see the day when Google is actually rewarding good writing. Like never before, it is important to strive for meaningful copy. It means you should go easy on fluff words and adopt an expository style of writing. It is also a good idea to do entity research when creating copy — including relevant entities helps create context for your content.
For more tips, check out this guide on using entities in SEO.
8. Core Updates
Date: 2017-present
How it works: As far back as 2017, Google has started to refer to bigger updates as Google core updates. Since then, there is even less transparency about what those updates are and which parts of search they are intended to improve. SEOs would often track post-update ranking shifts and try to figure out what exactly has changed, but there is rarely a conclusive observation. It is likely that Google core updates are just improvements on previous Google updates or perhaps bundles of smaller updates tied together.
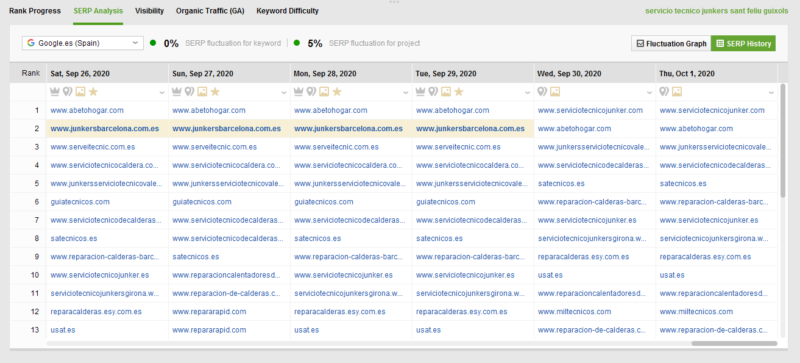
How to adjust: Since the effects of Google core updates are often unknown, one thing you can do is track SERP history for the keywords you are targeting. Once the update happens, you can check which of your competitors have moved up or down in rankings and make an educated guess about the contributing factors.
To start tracking your SERP history, launch Rank Tracker, go to Target Keywords > Rank Tracking > SERP Analysis, and click Record SERP data. The tool will start tracking the top 30 SERP positions for each of your keywords.