8 major Google ranking factors — SEO guide
Of over two hundred Google ranking factors that we know about, which ones are the most important? Here is the definitive list.
The SEO community is always looking for new ranking factors and we have discovered over two hundred of them so far. But there may be hundreds more actually used by Google. Luckily, we don’t have to work on all of them. Most have very little weight in SEO and are often used as tie-breakers rather than ranking signals. Instead, here is the definitive list of Google ranking factors, each of which can make or break your search optimization strategy.
1. Backlinks
Even though Google is planning to move away from backlinks in the future, they still remain the most important ranking factor for your pages. Except it is now too risky to use black hat SEO strategies — your links have to come from a variety of high authority websites that are similar to yours. Furthermore, some Google patents say that freshness and traffic may also be important backlink metrics.
Optimization strategy
The most efficient way to grow your backlink profile is to borrow backlink ideas from your search competitors. All you have to do is launch SEO SpyGlass, go to Domain Comparison > Link Intersection, and add a few of your top competitors. The tool will analyze your competitors’ backlinks and find the backlink gap — websites that link to your competitors, but not you. Those websites are your prime outreach targets. Seeing how they already link to other websites in your niche, they are very likely to host your links as well.
2. Semantic saturation
Your SEO content has to contain an appropriate amount of relevant keywords, entities, and images for the length of the copy. The content should not be stuffed, like in the old days of SEO, it should rather be a natural-sounding copy written in an informative style.
Optimization strategy
It could be a little challenging to figure out exactly which keywords to use, where to put them, and how many of them are needed. So, if you want to play it safe, a good strategy is to create a benchmark by analyzing your search competitors’ top-ranking pages. To do this in Website Auditor, go to Content Analysis > Content Editor, enter your main keyword, and get a detailed list of SEO writing instructions. The SEO Content Editor tool will tell you the right amount of main and secondary keywords, their placement, and the recommended length of the copy.

3. HTML tags
HTML tags tell Google which bits of your copy are the most important. The title and meta description tags are what users see in search results – write them like a keyword-rich promo. Heading tags (H1-H6) split your copy into sections — they should also contain keywords and be written in an informative style. Finally, alt text is used to describe images to search engines and should be filled out if you want to appear in the image search results.
Optimization strategy
If you weren’t mindful of HTML tags, then there are probably hundreds of pages on your website that are not properly optimized for search. A thorough approach would be to use Website Auditor and review your pages in bulk. First, go to Site Structure > Pages > On-page and sort the pages by their search optimization score. If you spot any pages with a low score, click on them for a detailed report. It will tell you exactly which HTML tags are in need of optimization and what’s wrong with them.
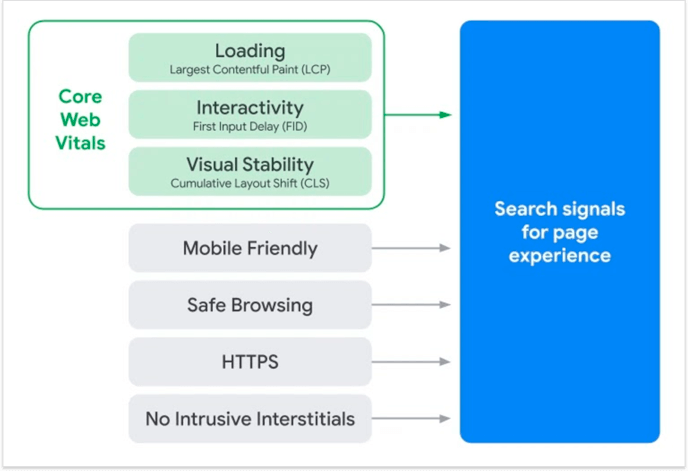
4. Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are the newest user experience metrics that will soon become Google ranking factors. The metrics will measure the first impression the user gets when visiting a page. Specifically, how fast it loads, how soon it becomes interactive, and how stable the layout is. Now, it’s important to note that the vitals are not yet official Google ranking factors. But they definitely will be, so it’s best to use the remaining time to get them into proper shape.
Optimization strategy
Google has been kind enough to equip each vital with a detailed set of optimization guidelines. For faster loading, Google recommends better server response times, less render-blocking JS and CSS, and faster resource loading. For improved interactivity, Google recommends code splitting and using less JS. Finally, for better visual stability, Google recommends using size attributes for images and videos and loading content from the top.
5. User behavior
There is a lot of uncertainty in the SEO community on whether Google actually uses behavioral metrics to rank pages. Google says that it doesn’t, but there’s been some pretty convincing evidence that it might.
The metrics we are talking about are the click-through-rate (CTR), bounce rate, session depth, and session duration. To check your performance on user behavior metrics, use your
Google Analytics and Google Search Console accounts.

Optimization strategy
Improving user behavior metrics has a lot to do with creating engaging content. For example, CTR relies on having an attractive snippet in search results. Meanwhile, bounce rate, session duration, and session depth rely on whether there is anything fun to do on your page. To keep users engaged, make sure to produce high-quality copy with plenty of visuals and internal links. The goal is to catch the visitors and send them down your sales funnel.
6. Structured data
There are thousands of tags to choose from, and they can tell Google every little detail about your content. Structured data can be used to tag authors, ratings, product features, locations, and so much more. And it can do wonders for your SEO — create links between entities, pin your location, and enhance your search snippets with rich elements:
Optimization strategy
If you are not a technically inclined person, then it’s best to use Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper. Choose the type of markup (article, local business, and product come highly recommended) and submit a link to the page you want to enhance. Now highlight bits of text and choose corresponding tags. When done, save the HTML file and upload it to your website. Extra step — check whether your structured data actually works with the help of Google’s Rich Result Test.
7. Google My Business listing
Claiming, optimizing, and maintaining your Google My Business listing is the single most important thing you can do for your local SEO. It helps establish your company as an entity, which in itself is a great asset to your SEO. More importantly, it skyrockets your local search performance. Once you create a listing, it becomes eligible for the local business panel as well as Google maps, opening your business to nearby searchers:
Optimization strategy
First, you have to visit Google My Business and either create or claim your profile. You will be asked to provide a few basic details as well as verify your ownership. When done, you will be transported to your Google My Business dashboard, where you will find many additional ways to enhance your listing. The least you can do is add a description, business hours, and photos, but there are many more cool features to explore. Google is constantly adding new Google My Business features and it’s gotten so advanced that it’s almost like a website of its own.
8. Mobile optimization
Mobile-first indexing is fully rolled out. Google announced that starting from September 2020 all websites without exception will be judged on their mobile version, not the desktop version. So, if you want your website to have any chance of ranking in search results, you have to make sure that it is designed for mobile users.
Optimization strategy
To check whether your page is mobile-friendly, visit Google’s mobile-friendly test, and submit a URL. If the page is ok, you will get a green light, and if it’s not, you’ll get some suggestions on what to improve.
Checking your website page by page is hardly practical, so you can use Google Search Console to check all your pages at once. Launch the tool, go to Enhancements > Mobile Usability, and view a report along with a list of suggested improvements.
Final thoughts
It’s important to keep tabs on the ever-evolving Google algorithm. Some ranking factors, like keywords and backlinks, are gradually losing importance. Other ranking factors, like user experience and semantic saturation, are taking their place. For now, though, the list above is a pretty solid selection of tactics to add to your SEO strategy.